
Anticipation Within Novartis
What is a guy who spent eight years selling food for Heinz doing at the top of the world's best research-based drug company? Preparing for the worst
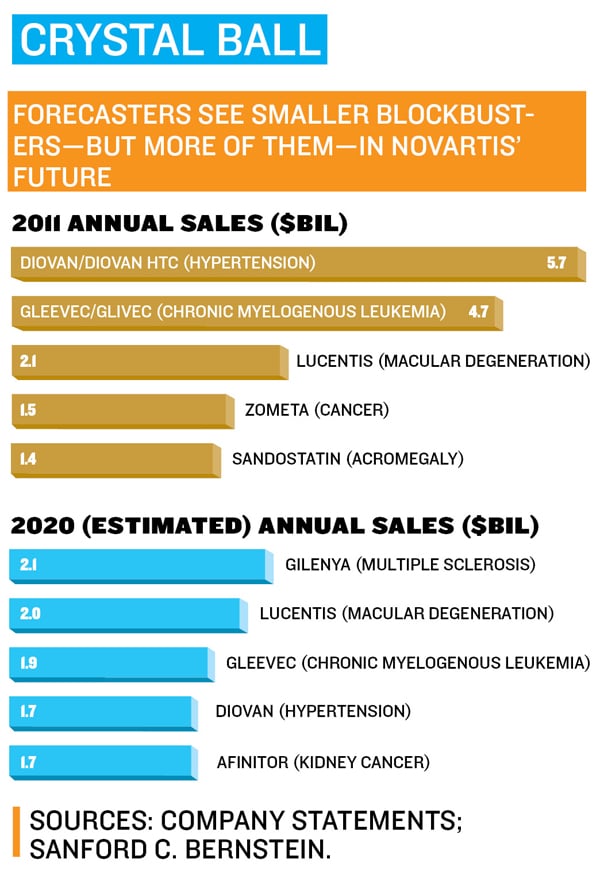
When you ask around the drug industry who the best leader of the last two decades was, Daniel Vasella’s name always comes up. He built Basel-based Novartis from an also-ran into the most respected drug research laboratory in the pharmaceutical industry. His 14 years running the company are legendary, with a record of drug development successes unmatched by any other chief executive over the past decade. His string of hits included cancer treatments Gleevec, Zometa and Diovan, part of a stable of blockbusters that accounts for more than $16 billion a year in revenues and helps millions of patients a year fight illnesses like leukemia, diabetes and breast cancer.
So when he chose a successor in 2010, many were surprised that he picked the ketchup guy.
Joseph Jimenez Jr., 52, had been with Novartis a little more than three years and was arguably the least scientific executive in the company’s C-suite when Vasella named him CEO. Before joining the drugmaker in 2007 he’d spent eight years running the US, European and then Asian operations of HJ Heinz, the maker of the world’s most popular ketchup. Even Jimenez was surprised by his spectacular rise. But Vasella had no doubts. “We have a lot of great scientists and a lot of physicians,” Vasella once told him. “Look at the way the world is changing. We need someone who can understand that.”
Turns out, Jimenez says, Vasella, now chairman of the company and still a major force in setting strategy, was right. Selling ketchup, organic baby food and tuna was the right preparation for dealing with the chaos ripping through healthcare right now. From exploding costs to tougher FDA safety regulations to patent expirations to ObamaCare, perhaps no other industry is currently experiencing such tumult.
Novartis has its own problems, too. Prospects for multiple medicines have been dashed by bad clinical trial results. Manufacturing problems hurt its generic and over-the-counter divisions, which include brands like Excedrin, TheraFlu and Triaminic. This September the US patent expires on Novartis’ top seller, the blood pressure drug Diovan, worth $5 billion annually, the biggest expiration the company has faced since being formed by a merger in 1996. Jimenez is unfazed. “If you look at my background in understanding the consumer,” Jimenez says, “it’s not just about marketing.
Consumer goods companies have to be very externally focussed, looking at their environment and how it’s changing all the time. What I have learned is that this is an industry that is changing so fast and so significantly.”
Novartis, he says, has prepared for the turmoil by diversifying like a packaged-goods company. Now he has to prove the plan will work, delivering on promises that sales will stay at their current $58 billion level and then growth will return. Novartis’ labs are delivering new drugs. But other companies are betting on spinouts, not diversification. Pfizer is shedding its veterinary and baby formula divisions, and Abbott Laboratories plans to literally split itself in half. Novartis is going in the opposite direction.
So far the strategy is showing promise. The Alcon eye unit, for instance, purchased in a series of deals totaling $52 billion, is growing 10 percent a year thanks to a worldwide increase in cataract procedures. In emerging markets like China and Russia he’s beefed up sales efforts. Over-the-counter brands are now growing at 20 percent in those countries. Even Novartis’ intermittently profitable vaccines unit, focussed on manufacture of commodity flu shots, could stay in the black once a new inoculation for meningitis hits the market in Europe this year.
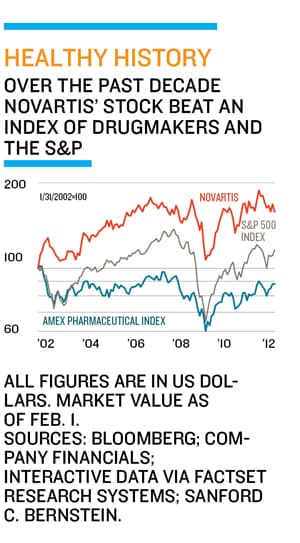
Wall Street remains unconvinced. Since hitting a five-year high last May shares have fallen 14 percent. Brian Lester, a buy-side analyst at Manning & Napier, likes Jimenez. “The consumer products companies went through a period that you could argue the drug companies now face over the next decade,” he says. “Growth slowed, they focussed on efficiency, and they deployed more of their resources into emerging markets. Isn’t that what the drug industry faces?” Still, he thinks the stock is overpriced.
Timothy Anderson of Sanford C. Bernstein says when Alcon is included Novartis has a better growth profile than any other drug giant, but warns of “headwinds” and says “the stock is in the dog house ... understandably.” Les Funtleyder, manager of the Miller Tabak Health Care Transformation Fund, owns Novartis but won’t buy more shares “unless the stock gets hurt more.”
So how did a baby-food-and-beans guy like Jimenez end up at Novartis? In 2002, after a career controlling household names from Clorox to Swiss Miss to Peter Pan peanut butter, Jimenez got on the board of healthcare giant AstraZeneca. There was talk of marketing but also developing cancer drugs and helping patients. “I loved what I heard,” says Jimenez. “I wanted to get into healthcare.”
He did. Initially hired at Novartis to run the company’s over-the-counter division, within months Vasella handed him the core drug business. When Vasella decided to become chairman and elevate Jimenez to succeed him, he passed over a number of talented executives, including then chief operating officer and heir apparent Joerg Reinhardt, who now runs Bayer’s health care business.
Luckily, when it comes to science, there’s a lot that doesn’t need fixing at Novartis. Under Vasella, Novartis had the best record for getting new drugs to market in the entire drug industry. Over the past 15 years Novartis has had 21 drugs reach the US market, more than any other company and twice as many as GlaxoSmithKline, Eli Lilly or Amgen. Top-line sales have grown at a steady 13 percent clip.
Much of the success came from an early insistence that medicines be breakthroughs for at least some patients. “True unmet medical need trumps everything,” says research chief Mark Fishman. This strategy springs from the success of Gleevec, a leukemia drug that was approved in 2001.
Deborah Dunsire, then an executive in the company’s cancer division, remembers trying to estimate the market for the drug, which battles a rare disease called chronic myelogenous leukemia. “It’s probably not going to make a lot of money because there are so few patients,” she said.
She was wrong. It did make money. Partly because Gleevec helps patients live for many years, all the while taking the drug, sales have ballooned to $4.6 billion. When the Diovan patent expires, it will be the biggest drug at Novartis. And other companies, like Takeda, where Dunsire is now in charge of cancer drugs, have made rare-cancer drugs the centre of their research.
Novartis continues on the Gleevec model, developing drugs even when the market seems iffy or super-risky. Examples include Coartem for malaria and new medicines being tested for forms of deafness and autism. But while this model has resulted in a lot of new drugs, there are not many big sellers. Few Novartis products generate more than $2 billion a year. They’ll still offset the patent expirations, says Jimenez. “I don’t believe there won’t be other Gleevecs.” One candidate is Afinitor, for kidney cancer, which also appears to be useful for breast cancer.
But keeping a steady stream of new drugs coming is nearly impossible, as any drug company exec will tell you. “Sometimes it is so hard to get a big bunch of new compounds through an organisation that five years later they say, ‘What’s next?,’ ” says John LaMattina, the former head of research at Pfizer.
Bernard Munos of the InnoThink Center for Research in Biomedical Innovation in Indianapolis says he thinks Novartis is managing to keep up its innovation speed. He credits Jimenez with finding a clever way of controlling how much his topic-roaming researchers spend. Novartis spends $4.6 billion in research money for every new medicine that’s approved, says Munos, less than the $13 billion per drug spent by Pfizer or the $17 billion spent by AstraZeneca but still too much. Jimenez hiked overall research spending, Munos says, but then told scientists to individually cut their own budgets. “Cost-cutting never comes easily,” says Munos, “but he aims to do it while increasing the scope of Novartis’ R&D. The industry needs more of that kind of leadership.”
The past six months have provided plenty of reminders, though, that the Gleevec approach isn’t perfect. Ilaris, approved in 2009 to treat a rare genetic disease that causes fevers and deafness in children, generates almost no sales. The plan was that it would also be approved to treat gout, which afflicts 8 million Americans. The FDA rejected it in August because it boosts the risk of infections. Jimenez says it is just a matter of finding the right population of patients. In the meantime, Novartis started to test Ilaris to treat heart disease; scientists think the same kind of inflammation found in gout may make artery plaques rupture, causing heart attacks—a gamble that won’t pay off for years.
Since then Jimenez has faced crisis after crisis that called into question Novartis’ diversification strategy. In November, Jimenez got a warning letter from the FDA personally addressed to him scolding the CEO for unresolved manufacturing problems in the company’s generic drug division.
The FDA found the over-the-counter unit that makes Excedrin was producing pills broken or in the wrong bottles. Jimenez shut the plant, took a $120 million charge and has halted Excedrin shipments until the problems are fixed.
In January, it was revealed that a patient had died after taking Gilenya, the first pill to treat the nerve-destroying disease multiple sclerosis. Jimenez had touted the pill as a research victory, and sales had been increasing faster than any multiple sclerosis drug ever, hitting $494 million in its first full year on the market. Regulators worldwide are looking into its safety, and in Europe, patients’ hearts are being monitored the first time they take the medicine. Another MS pill, BG-12 from Biogen, is on its way, and analysts think that it is likely to be the first-choice treatment for patients.
Jimenez argues it signifies strength, not weakness, that he can face down all these problems and still forecast that sales will stay about the same in 2012 as in 2011, with a dip in operating profit. Novartis is expected to file no new drugs with the FDA or other regulators in 2012. In 2013, there should be seven, including new drugs for heart failure and hepatitis C.
“I knew exactly what I was getting into,” Jimenez says. “When Dan put me in charge of the pharmaceutical division, I saw 2012 then. It was very clear what we were going to be going through. Back then it seemed a long way away. We have had a lot of time to plan and to prepare.” For better or for worse, the wait is over.
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)





