
Forever Young: Ned David is challenging the ravages of ageing
Now on his fifth startup, Ned David has the blueprint for creating a lucrative biotech. His latest project: A company that will take on the ravages of ageing

Nathaniel David’s career has turned into a blueprint for success in biotech
Image: Timothy Archibald for Forbes
Image: Timothy Archibald for Forbes
Nathaniel ‘Ned’ David is sitting at a conference table in South San Francisco in blue jeans, a black T-shirt and Tevas, looking and sounding a lot like Keanu Reeves as he discusses his latest startup, Unity Biotechnology. The idea behind Unity—preventing ageing—sounds crazy, but it’s backed by dozens of scientific papers, the key two in Nature. There are ageing cells, called senescent cells, that build up throughout the body and contribute to what we think of as old age—things like achy joints, waning vision, even perhaps Alzheimer’s. Kill those senescent cells with drugs, David reasons, and people might be able to grow old without becoming infirm.
“Like, how awesome would it be?” asks David, a preternaturally youthful 50. “The problem is you have to take the first baby step to demonstrate it’s possible. That’s what chapter one is: Demonstrate in a human being that the elimination of senescent cells takes a heretofore inescapable aspect of ageing and can either halt it or reverse it.”
Unity’s chief executive and chairman, Keith Leonard, 56, interrupts. “Just that,” he says sarcastically, aware that even his partner’s baby step sounds like a giant leap. “It’s easier to talk to the Food & Drug Administration about treatment of a disease once it’s diagnosed than it is to work really early and prevent disease,” Leonard admits. “But [prevention] is what we’d love to get to.”
It’s an amazing goal, backed by great science, not to mention $222 million in venture capital and $85 million raised from a May initial public offering, which valued Unity at $700 million, flat with its last fund¬raising. But achieving that goal also entails incredible risk. When a medicine is just beginning human tests, the odds it will make it to market are 10 percent. But since he was a doctoral student at Berkeley, David’s career has turned into a blueprint for success in biotech, transforming ideas from university laboratories into viable companies, investment gains and, maybe, drugs. David’s five companies have raised $1.5 billion and made investors close to $2 billion without ever actually turning a profit.
“He’s probably the best person in the world at finding great academic science and shaping it into a fundable story and a sellable business plan,” says Kristina Burow, managing director at Arch Venture Partners. She has known David since he was in graduate school and has backed four of his startups.
David has even made it to biotech’s finish line—an approved drug—twice, first with a diabetes drug from his first startup and again with Leonard as his CEO. Their previous company, Kythera, was sold to Allergan for $2.1 billion in 2015. It developed a shot, called Kybella, that destroys double chins. David and Leonard have both had the injection, and it probably makes them look younger. But can they combat the wear and tear of ageing in a fundamental way?
David received an undergraduate degree in biology at Harvard and a PhD in molecular and cellular biology at UC Berkeley. He remembers that time as “the most thoroughly enjoyable period in my life”, splitting his efforts between science and triathlons. In his last year as a grad student, just before he turned 31, he started his first company, Syrrx, which aimed to use cutting-edge biology to develop drugs. It raised $79 million from venture capitalists and was sold to Takeda for $270 million in 2005. David likely made a few million bucks. One Syrrx drug, Nesina, was approved in the US as a diabetes treatment in 2013.
After Syrrx, he was on to new projects, working on two companies at once as an entrepreneur-in-residence at San Francisco VC firm Versant Ventures. The first, founded in 2002, was Achaogen, an antibiotics company that went public in 2014 and currently has experimental drugs in late-stage trials. The second was Kythera, the company with the chin-fat drug. The idea was to apply a more rigorous scientific lens to the aesthetics industry.

Image: Image: Timothy Archibald for Forbes
Kythera turned out to be life-changing, because it gave David a long-term business partner: Leonard, who became Kythera’s chairman and chief executive in 2005. Cami Samuels, a biotech venture capitalist then at Versant, introduced them. Leonard, David says, figures out how to execute his wild brainstorms. “A lot of time in my life I felt judged for the things I wasn’t good at,” David says. With Leonard, “I’m allowed to be the person I am.” He adds: “The best professional time in my life is being able to work with Keith.”
At Kythera, David tried to hit lots of home runs. Three drugs failed, including a project partly funded by the CIA that would have created a substance that could be used to fundamentally reshape someone’s face, perhaps even making him or her look like someone else. As the focus narrowed on Kybella, the chin-fat drug, David’s attention wandered. In 2009 he helped hire his replacement as chief scientific officer and left to work full-time as a venture partner at Arch, where his penchant for big ideas meshed well with the go-big-or-go-home tendencies of Arch madman Robert Nelsen, who ranks fifth on Forbes’s annual Midas List of the top VCs.
David’s first Arch company, Sapphire Energy, was his worst bet. The idea was to use algae to make a substitute for petroleum, but even as the science succeeded, oil prices plummeted, making the economics unworkable.
The idea for Unity arrived in David’s email inbox in 2011, from multiple senders at the same time. It was a Nature paper from the Mayo Clinic laboratory of Jan M van Deursen. Van Deur¬sen had genetically engineered mice so that many types of senescent cells would die. The results of this experiment and of others that followed were striking. Mice in which the senescent cells had built up became withered and shivery, with kidney dysfunction, cataracts and bent spines. The ones without the senescent cells stayed hale and hearty for their whole lives, though they didn’t live any longer—all the mice still died by the time they were three. But the ones with fewer senescent cells stayed healthier until they dropped dead. They are the mouse version of Supreme Court justice Thurgood Marshall’s famed comment on when he planned to step down: “I expect to die at 110, shot by a jealous husband.” Senescence-targeting drugs, if effective, would make people live better, not make them immortal.
Van Deursen introduced David to Judith Campisi, at San Francisco’s Buck Institute, who had helped establish the senescent-cell field. She’d initially worked on cancer and became interested in the cells’ role in ageing because it helped her to get a scientific grant in the 1990s. Initially a sceptic, she found that the senescent cells were churning out chemicals that might help cause ageing. Arch founded Unity in 2011, with Van Deur¬sen and Campisi as co-founders. For five years the company didn’t even have offices; all the work was done at the scientists’ labs.
“For a basic scientist, we always dream our basic research is going to do some good, but in fact it almost never happens without a company,” Campisi says. “Ned is smart and he’s charming and he can convince you of lots of things, so he convinced me to join forces with him.”
In the 2015 sale of Kythera to Allergan, David, who’d already sold thousands of shares, grossed $30 million, Leonard $50 million and Arch $120 million. David says he’d been calling Leonard constantly for advice. With Kythera off the table, they could be back together at the same firm. Leonard took over as chief executive and chairman of Unity in 2016 (David describes it as “a relief”) and promptly raised $151 million from investors, including Arch and WuXi PharmaTech, a giant Chinese drug-research outsourcer. Unity raised another $60 million before its IPO; Unity execs say public investors were eager to participate. Still, the stock has dropped by 20 percent since it was listed on Nasdaq.
There’s a good reason for the scepticism, no matter how cool Unity’s science is: Investors have been hoodwinked by anti-ageing science before. In 2007, a company called Sirtris went public based on the hype around anti-ageing compounds related to red wine. GlaxoSmithKline bought Sirtris for $720 million in 2008, but it never resulted in any drugs and was shut down in 2013.
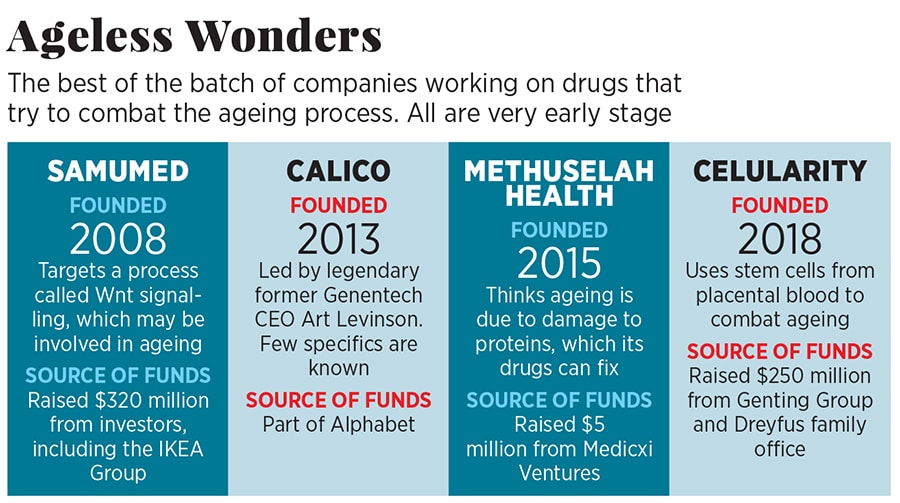
Then, two years ago, Samumed, a San Diego anti-ageing company, managed to raise $320 million at a valuation as high as $12 billion and to secure a Forbes cover. Its anti-ageing drugs have yet to live up to expectations. Unity, priced at a 20th of that, is certainly cheap by comparison. The executives have skin in the game: David owns some $50 million worth of the company and Leonard $30 million.
Unity needs to show that a medicine can have a clear effect in humans. Its first attempt, UBX0101, will target arthritis. When cartilage has been taken from patients during knee-replacement surgery, the medicine has helped it regrow in a dish. Now, in the first human test, it will be injected into the knees of 30 patients, who will fill out surveys about how much pain they feel, have fluid removed from their knees and undergo MRI scans. They’ll be compared with ten patients who will get a placebo injection. Any signs that the drug is making patients better will be seen as a reason to move into further studies. Unity expects to enter two more drugs into human studies by the end of next year. Candidate diseases include glaucoma, where killing senescent cells seems to lower the pressure that builds up in the eye, and lung dis¬eases, where it may coax lung cells to stop making scarred, fibrous tissue. Unity has raised so much money precisely because its executives know it may take multiple tries to find a medicine. It’s not known what the risks of killing senescent cells are; it’s possible they could include, for instance, slower wound healing. There’s no way to know until human tests begin.
Drug development is merciless, but that’s not stopping David from thinking even bigger. As Leonard builds a company around him, David is regularly meeting with a team of five in his office—which lacks a desk but has a mountain bike hanging by the window—talking about other types of potential technologies that could make ageing less painful. “There’s enough to keep me busy for the next ten years,” he says.
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)
X




