
Space tourism, on a budget
XCOR proves that you don't have to be a billionaire to break into the space tourism industry. Some clever lease-financing skills will do
The private space industry is a billionaire boys club. Elon Musk, Richard Branson, Paul Allen and Jeff Bezos have all founded companies that have spent tens of millions of their own and investors’ money to get into orbit.
Then there’s XCOR Aerospace, a startup in Mojave, California. Its founders aren’t rich, and they’re so thrifty that they often buy machinery on surplus websites for pennies on the dollar. Its every milestone has been bootstrapped with side contracts and pre-sales of tickets to space tourists. Yet if all goes to plan, the underdog XCOR may be the first company to take a paying customer into space in a privately built spaceship.
Construction on XCOR’s Lynx rocket plane is almost finished (in a hangar right next door to where Branson is building Virgin Galactic’s SpaceShipTwo). The company aims to begin test flights later this year. Give that stage six to 18 months before the Lynx will be ready to take passengers. To be sure, Virgin is a little ahead right now, having already completed several test flights and aiming for a suborbital test flight by year-end. But in the space industry, where progress is made two steps forward and one back, the timetables are pretty close.
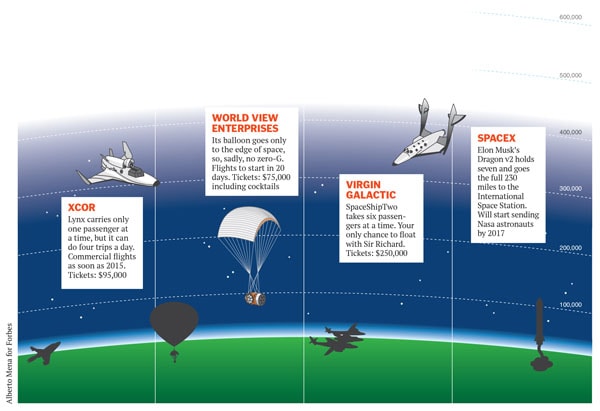
Like Virgin, XCOR offers a trip to suborbital space, but the experience is different and the price lower (not that space tourism is particularly price-sensitive). SpaceShipTwo holds six passengers, who have each paid $250,000 per ticket. The ship is carried by airplane to high altitudes before its rocket fires, hurtling the craft into space and allowing the passengers to float around weightless before descending to land on a runway. The Lynx holds only the pilot and one passenger, who paid $95,000. It takes off from a runway, whereupon its four rocket engines, each with 11,600 pounds of maximum thrust, take it to space in minutes. The passenger will experience weightlessness but remain strapped in. For a portion of the flight the passenger can act as a co-pilot, telling the pilot to perform different maneouvers to get a better view.
The company made history in 2001 when it flew its EZ-Rocket, the first privately-built and flown rocket-powered airplane. Share sales to wealthy friends helped fund that first project. Its second rocket plane, the X-Racer, was commissioned in 2005 by the Rocket Racing League, a group developing Nascar-style races for rocket planes. Its was the first rocket plane to feature XCOR’s piston pump engines, which can withstand 5,000 flights before being scrapped.
When it comes to government contracts, XCOR has a strict philosophy: The work has to be commercial in purpose, or the company will walk away. In 2003, XCOR signed a $750,000 contract with the Defense Department’s advanced research arm to develop pumps for propulsion engines. In 2005, it won a $7 million contract with Nasa to develop a liquid oxygen tank. Both helped XCOR develop its rocket designs.
XCOR’s business model took a new turn in 2008 when Andrew Nelson came on board as COO just as the credit bubble popped. XCOR had to lay off half of its staff, and executives went without salary for 14 months. Nelson, a former aerospace engineer-turned-investment banker, came up with the clever idea to borrow the “wet lease” concept from the airline industry. In a wet lease, the plane manufacturer finances the aircraft and provides crew and maintenance. All the airline does is the sales and marketing. In 2008, XCOR signed a deal with Space Expeditions Corp of the Netherlands, whereby Space Expeditions will sell tickets for suborbital flights on Lynx aircraft that are owned and operated by XCOR. Nearly 300 tickets have been sold at $95,000 each, providing XCOR with enough cash to develop the Lynx. Additionally, as part of the wet lease agreement, Space Expeditions makes set payments to XCOR as the Lynx hits certain milestones in its development. XCOR is also getting paid to develop a second-stage rocket with the United Launch Alliance, a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin that launches military payloads.
To date the company has grossed about $50 million and raised another $28 million in equity plus $10 million in incentives to move its corporate headquarters to Midland, Texas. Compare that to the financing behind Virgin Galactic, which has raised $390 million by selling a 38 percent stake to Abu Dhabi’s Aabar Investments and accepted more than $70 million in deposits from approximately 580 individuals.
XCOR’s CEO, Jeff Greason, shrugs. “Having more money doesn’t necessarily speed up the solution to your fundamental technical challenges.” That leads to the other question he gets a lot: Are you going to beat Virgin into space?
“I’m not sure anybody ever believes the answer, but the truth is, I don’t think about it, and I don’t care. We’re in a race with physics and economics. Not with the neighbours.”
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)





