
Moderna, racing for profits, keeps Covid-19 vaccine out of reach of poor
After developing a breakthrough vaccine with the financial and scientific support of the US government, Moderna has shipped a greater share of its doses to wealthy countries than any other vaccine manufacturer
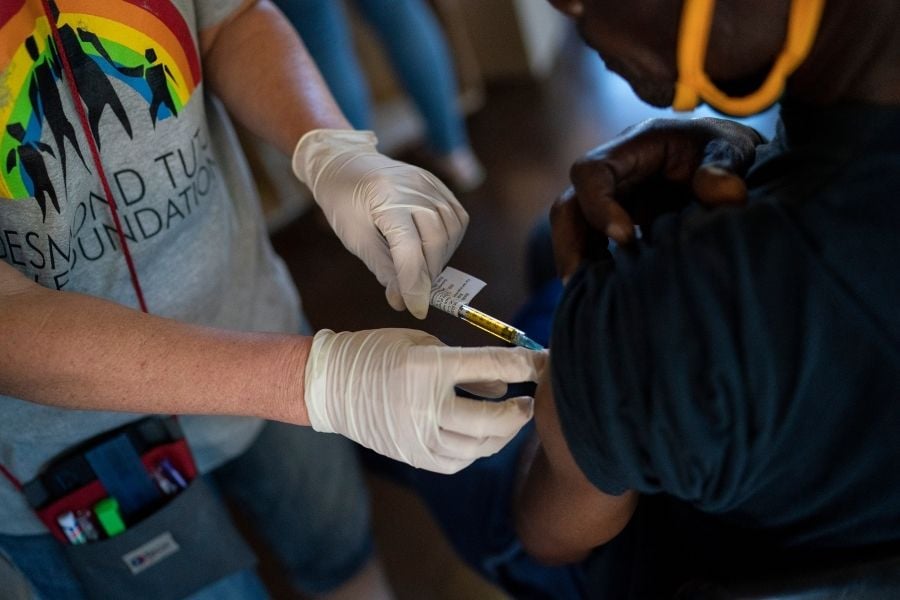 FILE — A nurse carries out trials of a COVID-19 vaccine at the Desmond Tutu HIV Foundation Youth Center in Masiphumelele, South Africa, Dec. 4, 2020. Moderna, whose coronavirus vaccine was developed with the financial and scientific support of the US government, has been supplying its shots almost exclusively to wealthy nations, keeping poorer countries waiting and earning billions in profit. Photo by Joao Silva/The New York Times
FILE — A nurse carries out trials of a COVID-19 vaccine at the Desmond Tutu HIV Foundation Youth Center in Masiphumelele, South Africa, Dec. 4, 2020. Moderna, whose coronavirus vaccine was developed with the financial and scientific support of the US government, has been supplying its shots almost exclusively to wealthy nations, keeping poorer countries waiting and earning billions in profit. Photo by Joao Silva/The New York Times
Moderna, whose coronavirus vaccine appears to be the world’s best defense against COVID-19, has been supplying its shots almost exclusively to wealthy nations, keeping poorer countries waiting and earning billions in profit.
After developing a breakthrough vaccine with the financial and scientific support of the U.S. government, Moderna has shipped a greater share of its doses to wealthy countries than any other vaccine manufacturer, according to Airfinity, a data firm that tracks vaccine shipments.
About 1 million doses of Moderna’s vaccine have gone to countries that the World Bank classifies as low income. By contrast, 8.4 million Pfizer doses and about 25 million single-shot Johnson & Johnson doses have gone to those countries.
Of the handful of middle-income countries that have reached deals to buy Moderna’s shots, most have not yet received any doses, and at least three have had to pay more than the United States or European Union did, according to government officials in those countries.
Thailand and Colombia are paying a premium. Botswana’s doses are late. Tunisia could not get in touch with Moderna.
©2019 New York Times News Service







