
What customers need to hear from you during the COVID crisis
Many brands have turned off their marketing efforts during the pandemic, but Jill Avery and Richard Edelman argue that now is the time when customers need to hear from you most. But what do you say?
 Image: Shutterstock
Image: Shutterstock
As the COVID-19 virus pandemic began to sweep across the world, Doug McMillon and his team at Walmart watched in horror. Suddenly, they realized, tomorrow would be nothing like “business as usual” and everything in the company’s marketing plan, from retail execution to advertising creative and media, would need to be rethought.
Recognizing that their existing brand creative might strike the wrong tone with people fearful for their own and their community’s health, and anxious about their personal and the world’s rapidly deteriorating economic situation, the Walmart marketing team pivoted quickly to produce and air new advertising creative that tapped into the rapidly changing zeitgeist. The result, the Retail Heroes campaign, featured CEO McMillon Zooming in remotely from home to thank the one million Walmart front line employees for their dedication to their work, he calls them heroes, not just to the company, but also to people around the globe.
At the same time, managers at other global brands were similarly considering their brands’ response to the COVID-19 crisis. Nike chose to twist its consumers’ athletic aspirations into a life-saving call to action with new ad copy that admonished, “If you ever dreamed of playing for millions around the world, now is your chance: play inside, play for the world,” to reinforce the need for people to stay home, while McDonald’s team in Brazil decided to redraw the iconic arches that made up the brand’s logo, drawing the two sides of the brand logo’s “M” apart to signal social distancing.
Many other Chief Marketing Officers (CMOs) pulled back from advertising during the crisis, going dark, fearful of offending or of being accused of taking advantage of an unfortunate situation for corporate gain. According to estimates from a March 2020 survey of marketers conducted by the Interactive Advertising Bureau, nearly a quarter of brands have gone dark, pausing all of their paid marketing communications for the first and second quarter of the year.
What’s the right strategy for a CMO during a crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic? During the week of March 23, 2020, Edelman, a global communications firm, conducted a survey of 12,000 consumers in 12 countries (Brazil, South Africa, Italy, France U.K., Germany, South Korea, Canada, China, U.S., Japan, and India) which were all in the midst of battling the novel coronavirus’s surge across the globe, to understand how consumers are responding to brand’s marketing during the crisis and to provide guidance to CMOs for branding in crises. These survey results form the basis for our analysis and advice below.
Do consumers want to hear from brands during a crisis?
Yes, they do, but only when that communication is comforting and reassuring to them and provides specific information about what brands are doing to respond to the pandemic. Consumers consider the brands they use to be trusted partners and look to them for information about the crisis and how it is affecting their companies, employees, and the products and services they provide. Brands should try to avoid communications that cause anxiety and concern about the crisis without offering solutions and hope to their consumers. And, brands should keep their consumers fully informed about how to continue to gain access to their products and services during the crisis, particularly for those deemed mission critical.
What do consumers expect from brands in a crisis?
Consumers expect quite a bit from their brand partners during a crisis, seeing them as critical partners to governments, non-profit relief organizations, and NGOs because of the powerful platform a strong brand delivers for communicating information and the strong relationships leading brands have with their consumers which may be leveraged to mobilize action. In fact, 63 percent of those surveyed believe that their country will not make it through the COVID-19 crisis without brands playing a critical role in addressing current challenges and 55 percent perceived that brands were responding more quickly and effectively to the pandemic than their government was, demonstrating the faith that consumers have in their brands and the companies that stand behind them. 86 percent of surveyed consumers view their brands as an essential safety net, ready to step up to assist anyone not helped by a government’s response to the virus, blurring the line between the private and public sectors.
Said Dr. David Nabarro, Special Envoy for COVID-19 for the World Health Organization (WHO), “Brands must strive to be authentic, accountable, and audacious in their communications. They should lead where they can and work together with NGOs and governments, recognizing that they have the capacity to jointly enact solutions.”
The core expectation that consumers have of brands in any situation, but particularly in a crisis, is that brands will do what is right for their employees, suppliers, customers, and society at large, without regard for how much it costs, with 90 percent of consumers stating that brands should be willing to suffer substantial financial losses to ensure the well-being and financial security of others. Those brands that do not run the risk of alienating a wide swath of consumers; 71 percent of those surveyed promised that brands and companies that placed their profits before people during the crisis would lose their trust forever.
How can brands help during a crisis?
- Educate the public by transforming the brand’s authority and media presence into reliable, factual information that instructs people about the crisis, how to protect themselves during it, and the progress being made to fight against it. For example, Unilever’s Dove brand released a video on social media that illustrated proper hand-washing techniques to help stem the tide of the virus at the same time its parent company announced $100 million in product donations, including 200,000 face masks to New York City hospitals to help keep healthcare workers safe. Given the prevalence of fake news proliferating in social media, consumers are looking to the brands they trust to provide the straight story.
- Offer free or lower-priced products to help people meet the challenges the crisis presents, particularly those most in need, such as healthcare workers or those forced into unemployment due to the changing economic environment. For example, Marriott’s and Hilton’s “Hotels for Hope” program offered free hotel rooms located near medical facilities to healthcare workers, while Serta Simmons donated 100,000 mattresses to hospitals as they frantically worked to increase the number of ICU beds during a surge in cases.
- Shift factories over from making consumer goods to products needed to fight the crisis. P&G used its factories to produce masks and hand sanitizer, while Ford and GE Healthcare teamed up to produce respirators and ventilators to help COVID-19 patients and support the stocks of overwhelmed hospital systems.
- Bring people together to help bridge the physical distance imposed by social distancing by facilitating community, offering empathy, and providing social support. AB InBev joined thousands of museums and performing arts organizations in offering virtual performances, sponsoring the Bud Light Dive Bar Tour: Home Edition featuring live music from popular artists livestreamed on YouTube, while Chipotle hosted Zoom hangouts where 3,000 fans could virtually mingle with celebrities. SnapChat curated mental health resources into a “Here for You” campaign, demonstrating its caring for its community of teenagers and young adults.
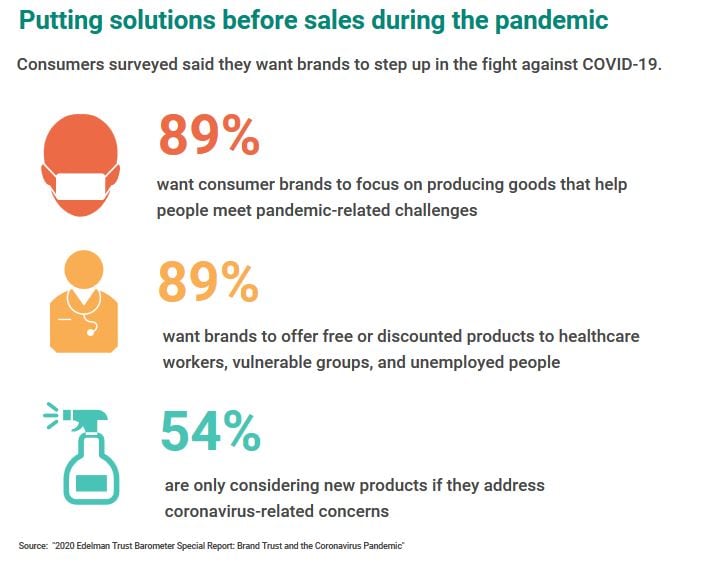
Which types of brand stories should companies tell?
After KFC was chastised by the U.K. Advertising Standards Authority for what it deemed inappropriate ads promoting the brand’s “finger licking good” behavior, many brands quickly turned off existing creative and searched for new brand stories to tell that better reflected the new cultural environment. Consumers largely agreed with this decision, with 77 percent claiming that brands in their marketing communications should not ignore or turn a deaf ear to the crisis, but rather make sure to recognize it and acknowledge the impact it was having on people’s lives.
Consumers also warned against brands taking advantage of the crisis. Consumers’ survey responses indicated that brand storytelling should focus on providing real solutions to the crisis rather than hard-core selling, with the request that brands work to connect their products and services to the alleviation of crisis-related suffering and challenges. 54 percent of surveyed consumers claimed they were ignoring all new product communications during the crisis, unless the product in question was specifically designed to help them with serious pandemic-related life challenges. Communications that were perceived to benefit the brand more than they benefited its consumers or ones that offered frivolous solutions rather than real ones raised consumers’ eyebrows, while programs that helped the brand’s employees or suppliers were applauded, such as Miller Lite’s virtual tip jar for bartenders or Yum Brands $1,000 bonuses to its Taco Bell, Pizza Hut, and KFC general managers during mandated restaurant closures and emergency medical relief fund for employees diagnosed with COVID-19.
Dr. Nabarro advises brands to be careful to check their facts before relaying them to consumers, pointing to respected health organizations, such as the WHO, as important sources. Consumers, increasingly skeptical as fake news proliferates online, are looking to brands to be the bearers of truth. He also recommends that brands not be distracted by or engaged in political debates, but work to bridge divides among people during the crisis.
Consumers also cautioned brands about using humor or brand stories that were too lighthearted in tone during a crisis, perceiving a mismatch between these types of ads and the international mood. While some (42 percent) advised avoiding escapist fantasies based on the way life was before the crisis, such as creative that featured people gathering together in large groups, others were more amenable to hopeful messages that featured a return to normal, such as Guinness’s well-received mid-March ad, which promised its consumers a better future where “We’ll March Again” after the cancellation of many St. Patrick’s Day parades.
The risks are large for marketers who get brand storytelling wrong during a crisis. Derogatory memes proliferated after a group of celebrities, including Gal Gadot, Jimmy Fallon, Natalie Portman, Cara Delevingne, and Will Ferrell, came together virtually to sing an inspirational version of John Lennon’s "Imagine." Instead of providing the soothing relief and entertainment the celebrities intended, the video, widely circulated on Instagram and on other social media platforms, incited anger that the celebrities seemed out of touch with people’s suffering as they quarantined in their multimillion dollar homes, and frustration that the celebrities were not using their brand platforms and influencer status to more meaningfully help those most in need. Surveyed consumers deem celebrities and social media macro-influencers to be less credible spokespeople for brands during a crisis, with most consumers favoring true expertise and expressing a desire to receive COVID-19 related brand information from a doctor or health authority, the brand’s technical experts, CEO, or founder, or a person more like themselves.
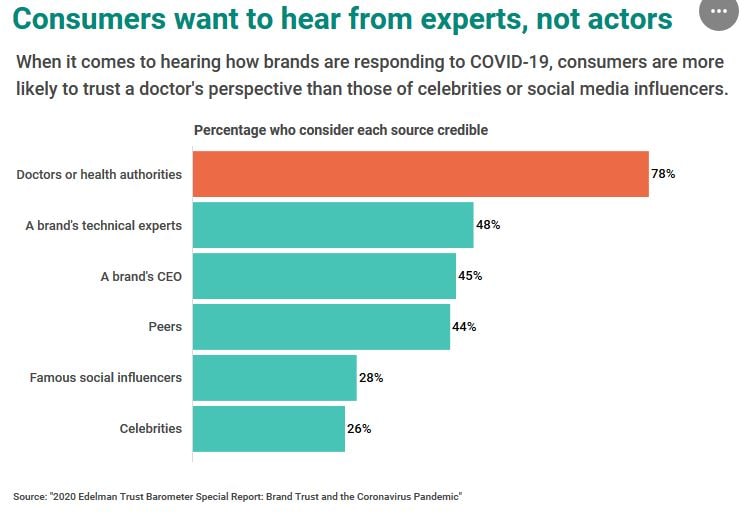
What should brands expect from consumers in a crisis?
Reflecting the power and platform provided to them via social media, 33 percent of surveyed consumers claimed that they were already punishing brands that were not responding well to the crisis by convincing others through social pressure to stop using them. However, marketers should take heart that despite a higher level of risk involved in communicating during a crisis, brands that do it well have the opportunity to reap significant rewards. 65 percent of surveyed consumers indicated that their likelihood of purchasing a brand would subsequently be based on how well the brand responds to the crisis. Crises may also provide a unique time for new brands to stand out in a crowded marketplace as a result of the innovative or compassionate ways they are responding to the virus outbreak, with 37 percent of consumers indicating that they had recently started using a new brand as a result of their crisis-related marketing efforts.
While trust has always been important to consumers, in times of crisis, consumers’ desire to patronize trusted brands increases, with 60 percent of consumers reporting that they were finding themselves turning toward brands that they are absolutely sure they can trust, perhaps providing a leg up to legacy brands and/or brands that have managed to nurture strong consumer-brand relationships prior to the crisis. The cocooning behavior promoted by shelter-in-place orders may encourage a return to brands that were trusted childhood favorites that could offer consumers mental transportation back to a simpler time.
The global COVID-19 crisis has drastically changed the way people are relating to each other, isolating us in our homes and pulling us away from our social milieu. It is likely to fundamentally change how we think, behave, and consume, in both the short term as we navigate the crisis and beyond. Says Dr. Nabarro, “There will be a new normal. We will have to live with the virus and the scars of the virus for a long time. We will all have a new sense of realization.” So too, is this crisis changing consumers’ relationships with and expectations of brands. At this moment of deepest need, the new world for brands will have trust at its core. The mandate to brands from global consumers is clear: step up and help, not just your own customers and employees, but the world at large; protect all, support and care for all, and innovate in the public’s best interest. Brands that respond to consumers’ clarion call with compassion and solution-based action that creates real value have a tremendous opportunity to reinforce trust and engender loyalty as they help to save the world. This is the true test for purpose-driven brand leaders, to respond in this crisis with compassion and empathy, to act based on facts, and to be part of the global solution.
About the Authors
Dr. Jill Avery is an authority on brand management and customer relationship management and a senior lecturer in the marketing unit at Harvard Business School, where she created and teaches the course Creating Brand Value. She is a former brand manager at Gillette, AT&T, and Samuel Adams and an advertising agency executive, and remains close to practice by serving as a board member, consultant, educator, and advisor to companies and their executives.
Richard Edelman is the CEO of Edelman, a global communications firm, named “PR Agency of the Decade” by AdAge. He has extensive experience in marketing and reputation management, having led assignments with major corporations, NGOs and family businesses in over 25 industries around the world. As the creator of the annual Edelman Trust Barometer, Richard has become one of the foremost authorities on trust in business, government, media and NGOs. Richard topped PRWeek’s list of most powerful executives (2013), was recognized as the third highest rated CEO by Glassdoor (2014) and was inducted in the Arthur W. Page Society’s Hall of Fame (2014).
This article was provided with permission from Harvard Business School Working Knowledge.







