
EXPLAINED: How an oil barrel became worth less than nothing
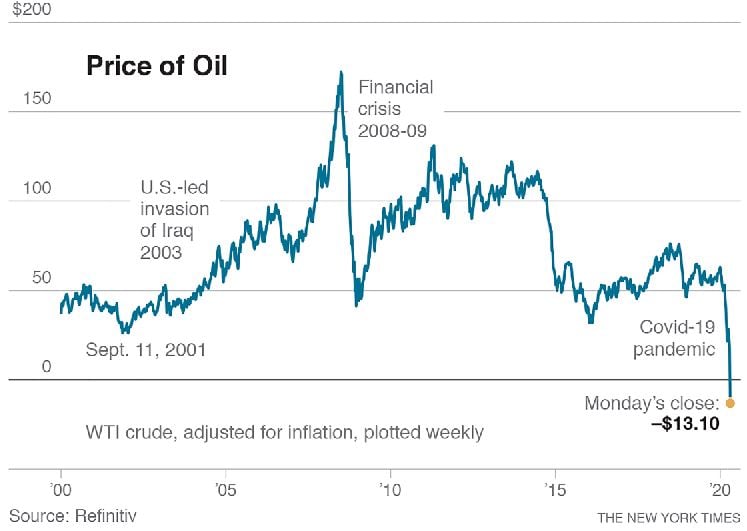
The price of the main US oil bench mark fell to end the day about $30 below zero, negative for the first time ever . Such an eye-popping slide is the result of a quirk in the oil market, but it underscores the industry's disarray as the coronavirus pandemic decimates the world economy
 An essential employee of NY Tire Center in New York, April 18, 2020.
An essential employee of NY Tire Center in New York, April 18, 2020.
Image: Desiree Rios/The New York Times
Something bizarre happened in the oil markets on Monday: Prices fell so much that some traders paid buyers to take oil off their hands.
The price of the main U.S. oil bench mark fell more than $50 a barrel to end the day about $30 below zero, the first time oil prices have ever turned negative. Such an eye-popping slide is the result of a quirk in the oil market, but it underscores the industry’s disarray as the coronavirus pandemic decimates the world economy.
Demand for oil is collapsing, and despite a deal by Saudi Arabia, Russia and other nations to cut production, the world is running out of places to put all the oil the industry keeps pumping out — about 100 million barrels a day. At the start of the year, oil sold for over $60 a barrel but by Friday it hit about $20.
Prices went negative — meaning that anyone trying to sell a barrel would have to pay a buyer $30 — in part because of the way oil is traded. Futures contracts that require buyers to take possession of oil in May are expiring on Tuesday, and nobody wanted the oil because there was no place to store it. Contracts for June delivery were still trading for about $22 a barrel, down 16% for the day.
“If you are a producer, your market has disappeared and if you don’t have access to storage you are out of luck,” said Aaron Brady, vice president for energy oil market services at IHS Markit, a research and consulting firm. “The system is seizing up.”
 Something bizarre happened in the oil markets on Monday: Prices fell so much that some traders paid buyers to take oil off their hands.
Something bizarre happened in the oil markets on Monday: Prices fell so much that some traders paid buyers to take oil off their hands.Refineries are unwilling to turn oil into gasoline, diesel and other products because so few people are commuting or taking airplane flights, and international trade has slowed sharply. Oil is already being stored on barges and in any nook and cranny companies can find. One of the better parts of the oil business these days is owning storage tankers.
“Traders have sent prices up and down on speculation, hopes, tweets and wishful thinking,” said Louise Dickson, an oil markets analyst at Rystad Energy, a research and consulting firm. “But now reality is sinking in.”
The world has an estimated storage capacity for 6.8 billion barrels, and nearly 60% is filled, according to energy experts.
Some of the oil glut is evident in Cushing, Oklahoma, a critical storage hub where the oil that trades on the U.S. futures market is delivered. With a capacity to hold 80 million barrels of oil, Cushing has only 21 million barrels of free storage left, according to Rystad Energy, or less than two days of American production. As recently as February, Cushing was not even up to 50%. Now, experts say it will be filled to the brim in May.
Storage is almost completely filled in the Caribbean and South Africa, and Angola, Brazil and Nigeria may run out of warehousing capacity within days.
In his news briefing Monday, President Donald Trump said the government was “looking to put as much as 75 million barrels” into the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, which is used as a buffer during crises and was created after the 1973-74 oil embargo.
The reserve has about 635 million barrels of oil, and is equipped to store 75 million barrels more. But the reserve can take only about 500,000 barrels a day.
Congressional Democrats recently balked when the administration proposed spending $3 billion to fill the reserve as part of the stimulus package lawmakers passed last month. But on Monday, Rep. Lizzie Fletcher, D-Texas, said she would introduce legislation appropriating funds for a reserve purchase.
But it will be hard to quickly fix the oil industry’s problems. The oil infrastructure is complicated and it’s not easy to turn off the taps. In addition, countries like Saudi Arabia and Russia, whose economies are reliant on oil, only reluctantly cut production.
Shutting down oil wells and then restarting them when demand returns can require expensive manpower and equipment. Fields do not always recover their former production. In addition, some oil companies keep pumping, even if they are losing money, in order to pay interest on their debts and stay alive.
A little over a week ago, there was some optimism in the oil industry. The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, Russia and other producers said they would cut 9.7 million barrels a day of production, or about 10% of global oil output, the largest cut ever. It was a grim acknowledgment that global demand had collapsed.
But that record cut will not be nearly enough. Analysts expect daily oil consumption to fall by as much as 29 million barrels in April, about three times the cuts pledged by OPEC and its allies, and May isn’t expected to be much different.
“It’s relatively impressive in terms of the overall number, but it’s not enough to tighten the market between now and the fourth quarter of 2020,” David Fyfe, chief economist at Argus Media, a commodities pricing firm, said about the cut by OPEC and its partners.
U.S. oil producers are also reducing production, but not rapidly enough. At the current pace, American production will decline to less than 11 million barrels a day by the end of the year, from 13.3 million barrels a day at the end of 2019.
Such cuts should help stabilize the markets, but it might take months. The U.S. contract for oil delivered in May 2021 was trading on Monday at about $35 a barrel, hinting at how long it might take for prices to reach levels they were at just a few weeks ago.
The oil industry’s plight is forcing policymakers to consider intervening more forcefully.
And on Tuesday, the Texas Railroad Commission, which regulates oil and gas drilling, will take up a proposal for a 20% statewide production cut Tuesday. The commission used to regularly manage oil production but hasn’t done so since the early 1970s.
©2019 New York Times News Service




