The Cutting Edge in Indian Medicine
Minimally invasive surgery is an exciting, fast-growing area of healthcare. We look at four procedures you may not have heard of
Broken-down cartilage in the knee
When your body is cut open, whether by a knife-wielding lunatic or a skilled surgeon, it goes through trauma that the body must recover from. That is why medical science always seeks to do the body the least damage possible. Minimally invasive surgical techniques offer far shorter recovery times, and many are also cheaper than older methods.
Procedures like lasik eye surgery, and even major, life-saving ones, like angioplasty, have become mainstream. What other operations are gaining ground? We asked some leading doctors to tell us about procedures that are useful, but yet to gain major popularity.
We must urge you, however, to not take medical decisions based solely on what you read here. Self-diagnosis is dangerous, more so in this age of easy information dissemination and access, where unverified falsehoods have as much chance of being read as rigorously researched facts.
Educate yourself by all means, but remember that it takes many years of hard work and concentrated study before you can become a doctor.
Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI)
Cartilage is the tough, elastic tissue that serves as a cushion between bones. People such as marathon runners who perform repetitive motions may damage their articular cartilage, causing pain and stiffness in the knees.
Approximately one-third of the general population suffer from osteoarthritis and spondylitis of knees and spines Treatment for such injuries is not trivial and includes bone marrow stimulation techniques, abrasion arthroplasty (debridement), drilling, micro-fracture, and mosaicplasty. The cells generated by techniques like mosaicplasty and micro-fractures could break down after a period of time, and the pain experienced earlier could return.
ACI, was pioneered by Lars Peterson, in Gothenburg, Sweden, in 1987. The outcome was reported in the New England Journal of Medicine in 1994.
Cartilage harvested from the patient is subjected to enzymatic digestion, to isolate the cells called chondrocytes. These are live cells; various techniques are used in the cell culture lab to grow and multiply them. Then the joint is opened, and the area with the defect is prepared. The chondrocytes are mixed with fibrin, a very sticky substance, to form a thick clot-like mixture that sticks to the affected area, forming a scaffold for the cells to grow into the bone.
ACI uses cells harvested from cartilage, and not fibro cartilage that results from the more common micro-fractures (which develops as a result of bleeding) that breaks down. Another specialist told us that ACI is good for lifelong treatment, whereas with micro-fractures, the person may have to come back again for treatment in a few years.
The downside is that it is expensive: About Rs. 2.5 lakh. The basic cost of harvesting and growing chondrocytes starts at Rs. 1.5 lakh. Doctors hope that if hospitals start to culture these cells in their own labs, the cost might come down. Reliance Life Sciences, which is also looking into this area, said its cartilage regeneration initiative is undergoing clinical trials.
Case File
Five years ago, John Smith (name changed on request), 43, got a swelling in his knee that grew into severe pain over the next few years. An arthroscopic examination in South Africa revealed a small (2cm x 2.5cm) defect of the medial femoral condyle. After micro-fracture treatment for the lesion, he improved marginally for a short period, but found his very active lifestyle much hampered.
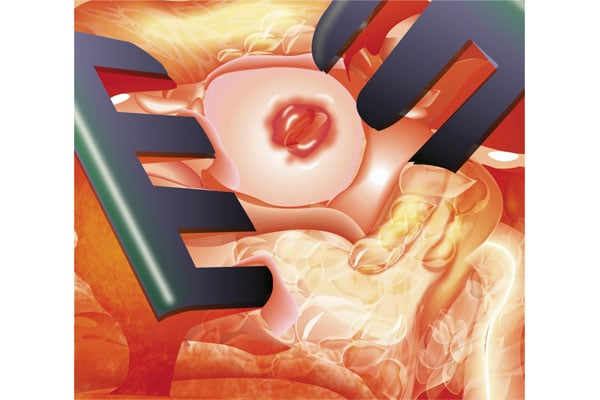

Broken-down cartilage in the knee
So, he came to India for an assessment; there, it was found that the micro-lesion had increased, not healed. Otherwise his knee was good. Since he was a well-built, active guy, it was inevitable that he would put a load on his knee. With painkillers, one option, he could become arthritic over time. ACI, he was told, may not cure him completely, but it was worth trying because of his activity level.
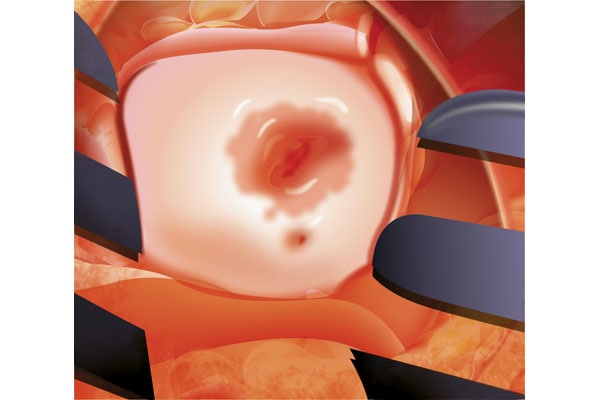
The affected area, now implanted with new chondrocyte cells and fibrin
He decided to go through with it, and had the procedure done at Fortis Hospital, Mulund, Mumbai. For six weeks after the procedure, he was not allowed to put weight on the leg; he remained in hospital for three months, undergoing regular motion exercise to target the isometric areas.
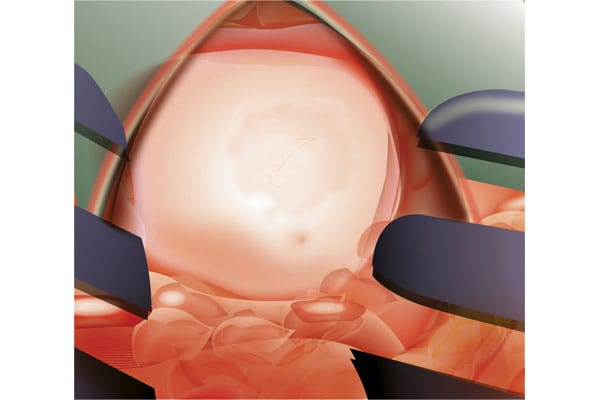
After healing
There was significant improvement, he said: If 10 was the level of pain he experienced before, it had been brought down to 1. He continues to do exercise for stiffness which developed over time, but the sharp pain was gone.
Second Opinion
Dr. Kaushal Malhan, knee and hip surgeon, Fortis Hospital, Mulund, Mumbai; previously worked in Robert Jones Agnes Hunt Hospital, a specialty orthopedic hospital, where two to three ACI surgeries were performed every week: “Often patients get fooled that anyone with arthritis can receive this treatment. It is primarily used for people where the damage is localised, and is not more than two to three centimetres.”
Dr. Manoj Sharma, senior consultant, orthopaedics and spine surgeon, Apollo, Delhi: “Only if the defect is in the weight-bearing area of the knee can ACI have some benefit to the patient.”
Ozonucleolysis or Ozone Discectomy
Slipped disc or, more accurately, spinal disc herniation, may occur when the outer layer of the disc between vertebrae degenerates and causes the soft inner portion to protrude. The condition can be very painful, not just in the back but also in other parts of the body, since nerves from the spine branch out; the worse the damage, the more the pain.
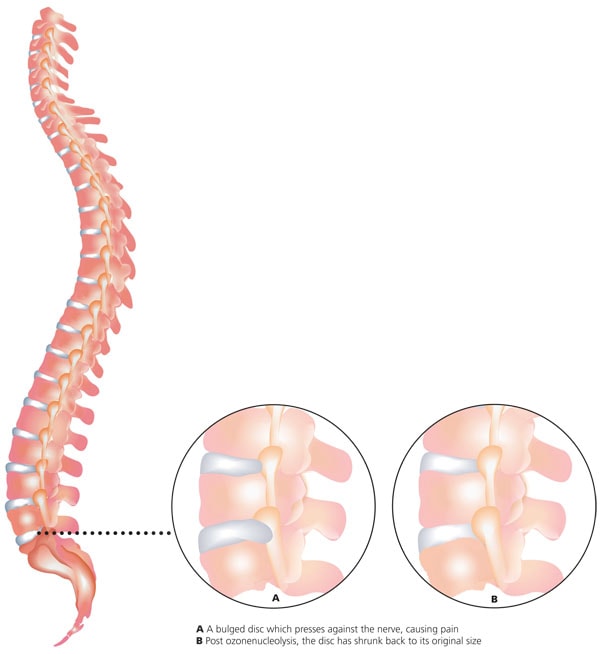 Approximately five percent of the general population is affected by spine problems. Traditional treatments include laminectomy, where you remove pieces of bone from the spine to make space for the spinal canal and nerves, and discectomy, where you remove pieces of the bulged or ruptured disc that are causing pressure on the nerves. Both are surgeries that need extended recovery time and costs of hospitalisation.
Approximately five percent of the general population is affected by spine problems. Traditional treatments include laminectomy, where you remove pieces of bone from the spine to make space for the spinal canal and nerves, and discectomy, where you remove pieces of the bulged or ruptured disc that are causing pressure on the nerves. Both are surgeries that need extended recovery time and costs of hospitalisation.
The first ozone generator was invented in Germany in 1857 by Werner von Siemens who founded a rather large company that bears his name. It took over a hundred years to be first used for the treatment of disc disease. In India, Dr. Vijay Sheel Kumar, neurosurgeon at Doctor Kares Hospital*, Gurgaon, first introduced Ozone Discectomy in 2003.
In the treatment, ozone is injected into and around the disc over a series of sittings. Ozone draws water out of the disc, molecularly decompressing it. It also has an anti-inflammatory and pain-killing effect, and thus can help the patient avoid surgery altogether.
Case File
Jeetender Yadav, 33, says, “I had a huge problem with my back, where my movement was frozen. At any cost, I wanted to avoid surgery [which] many doctors recommended.” So, even though ozone therapy was pretty much an untested treatment, still in clinical trials, Yadav decided to go ahead with this therapy.
Six months later, his Rs. 60,000 bet on the procedure paid off: “I could see the effect of the treatment immediately. I had to go for six sittings of the injections, and with each sitting, I could see an improvement of 10 percent, 20 percent, 30 percent and so on.”
Second Opinion
Dr. Vijay Sheel Kumar: “If a patient has a disc with bowel or bladder symptoms, immediate surgery must be considered before any other options.”
Dr. Manoj Sharma, senior consultant, orthopaedics, and spine surgeon, Apollo, Delhi: “Ozone therapy is mostly for people with a contained disc. Where the disc is not contained and there is a chance of leakage in canal, it should not be used.”
Robotic Surgery for Radial Prostatectomy
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland (part of the male reproductive system) mutate into cancer cells. Symptoms include frequent urination, painful urination, blood in urine, increased urination in the night.
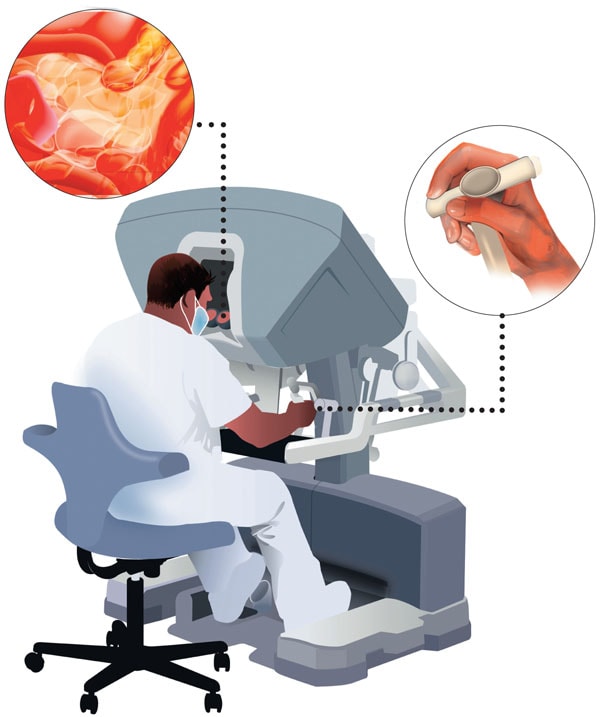
ROBOTIC SURGERY The da Cinci is one of the most popular surgical system in the world. The console gives the surgeon a three-dimensional view through a binocular viewport and interaction is through “masters” into which the surgeon inserts his or her hands
Approximately 4.6 per 100,000 of the population need treatment for prostate cancer. Traditionally, it has been treated with laparoscopic surgery, which does not have the precision that robotic surgery can give, and can result in a bit of the tumour being left behind.
The first urologic surgery with the assistance of a robot dates back to 1979.
In 1993, Computer Motion filed a patent for its Automated Endoscopic System for Optimal Positioning (AESOP), a robotic arm with motorised joints, which became the first active robotic device approved by the USA’s Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Devices like it have paved the way for others, like the very popular da Vinci Surgical system, manufactured by Intuitive Surgicals, USA.
A group of urologists in France started robotic radical prostatectomy in 1996, but it was popularised by Mani Menon from Detroit, USA, in 2001. Regular robotic urologic surgery started in India in the department of urology at AIIMS, New Delhi, under Dr. N.P. Gupta, who is now the chairman, Academic and Research, Urology, at Medanta Institute of Kidney and Urology.
Prostate surgery needs a very high degree of precision; inaccuracy can cause permanent change in a patient.
Dr. Alexander Kutikov, Assistant Professor of Urologic Oncology, Fox Chase Center, Philadelphia, says, “The prostate is intimately related to the urinary sphincter that is responsible for continence; nerve fibers that are responsible for erectile function basically ‘shrink wrap’ the gland, and the cancer lies on the outer edges of the gland and is easily left behind if the operation is not performed correctly. [..] A few elite surgeons were able to master laparoscopic prostatectomy, but it took many cases to achieve results that were comparable to a traditional prostatectomy.”
Previous surgical procedures could wind up not removing every trace of the cancer; it required great surgical skill to be able to have a successful surgery.
With robotic surgery, while success is still dependent on the surgeon’s skill, much higher precision is possible, increasing the chances of removing all traces of the cancer. “The human arm can only move 45 degrees to 90 degrees,” says Dr. Ramesh Mahajan, urologist, Fortis, Kolkata. “Robotic surgery allows for greater precision as the robot can move 360 degrees. It also allows for less tissue damage because of this level of precision.”
There are very few places equipped to handle this procedure, because of the high costs involved: The machine can cost Rs. 60 crore to Rs. 70 crore. AIIMS in Delhi and Medanta in Gurgaon are currently the only places in India with the machine.
Case File
R.S. Nanda, 69, had a carcinoma prostate in an early T2 stage. “I chose to have this procedure as it has a few benefits. It takes three hours by robotic surgery. Older forms of surgery would take six hours. And the time for recovery is longer in the old form of surgery and patient [can] experience incontinence.”
His surgery was done by Dr. N.P. Gupta at AIIMS and he has not had any side-effects or recurrence of the problem.
Second Opinion
Dr. N.P. Gupta: “The disadvantage of robotic surgery is the initial cost of equipment and the cost of reusable robotic instruments.”
Dr. Kutikov: “Costs at this point are higher than with open surgery; however, some argue that decreased time away from work/shorter hospital stays justify the added intra-operative expenses of the technology.”
Collagen Cross-Linking or C3-R Treatment
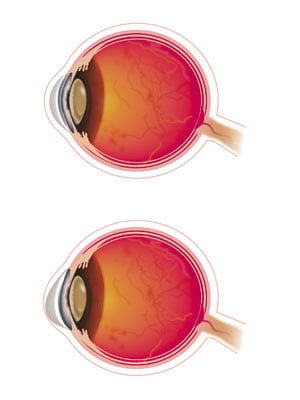
Keratoconus is a condition where the cornea turns from spherical to a more conical shape. For the patient, it means frequent changes in spectacles, with increasingly higher-powered lenses needed. Another indicator, say eye specialists, is frequent rubbing of the eyes. If not treated, it could result in an increased level of myopia and astigmatism.
It afflicts about 2.3 percent of the general population. Treatment has traditionally been through cornea transplants. But, as Dr. Rohit Shetty, vice chairman, Narayana Nethralaya, says, “There is a waiting period, and chances of failure with the transplant are high.”
With C3-R, the patient lies under a UV lamp for 40 to 50 minutes, and riboflavin drops are administered continuously. This forms a chemical bond which arrests further degeneration of the cornea and strengthens it.
“With collagen cross linking,” Dr. Shetty says, “I can bring down my waiting list for a transplant from 40 percent to 7 percent. Also, in patients whose cornea has progressive keratoconus, where they are close to 300 microns, and where surgery will not help, this technique is beneficial.”
Case File
Priya Prakash, 22, software engineer, consulted several doctors, but the verdict was unanimously grim.
 The normal thickness of the cornea is 480 microns to 500 microns; hers was 360 microns thick. There was nothing, they said, that would stop her cornea from getting thinner.
The normal thickness of the cornea is 480 microns to 500 microns; hers was 360 microns thick. There was nothing, they said, that would stop her cornea from getting thinner.
Collagen cross-linking, however, arrested the progression of the disease. Today, she leads a normal life and, with help from contact lenses, can see well again.
Second Opinion
Dr. Sridhar Baratan, general ophthalmologist, Shankara Nethralaya: “Collagen cross-linking is not the end-all result for treatment of keratoconus. This procedure does not work in all patients, and the waiting list for cornea transplant is not very long in hospitals.”
The cornea in its normal spherical shape and below that is a affected by keratoconus, the cornea has bulged to a more conical shape
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)