
Burger, King and the Crown
How Burger King became the fastest-growing QSR brand in India, but can it flip the Big Mac?
 Rajeev Varman, CEO, Burger King India
Rajeev Varman, CEO, Burger King IndiaImage: Selvaprakash Lakshmanan for Forbes India
It was the fag end of 2014, and Burger King was just getting started in India. One of the last big burger chains to set up shop in the country, the American brand opened its first outlet at Select Citywalk mall in South Delhi in November. No bun intended, but the Miami-based QSR giant, globally known for its flagship five-inch diameter burger ‘Whopper’ with seven layers, didn’t stand a chance against famed rival McDonald’s.
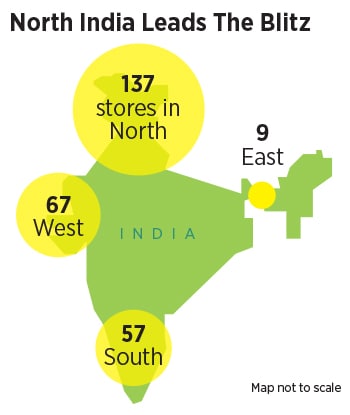 The reasons were many. In fact, seven. First, the Golden Arches entered India almost two decades before, in 1996. Second, the two franchisee partners of McDonald’s had over this period built up a beefy presence. By the end of March 2015, while Connaught Plaza Restaurants—running operations in North and East India—reportedly had some 150-odd outlets, Westlife Development, which managed the show in West and South India, was sitting pretty with 209 outlets. Burger King, in contrast, had 12. Third, for a player coming in so late, there was no real state available at prime locations. Fourth, brand awareness of the challenger brand was abysmally low. Back then, only 17 percent knew Burger King.
The reasons were many. In fact, seven. First, the Golden Arches entered India almost two decades before, in 1996. Second, the two franchisee partners of McDonald’s had over this period built up a beefy presence. By the end of March 2015, while Connaught Plaza Restaurants—running operations in North and East India—reportedly had some 150-odd outlets, Westlife Development, which managed the show in West and South India, was sitting pretty with 209 outlets. Burger King, in contrast, had 12. Third, for a player coming in so late, there was no real state available at prime locations. Fourth, brand awareness of the challenger brand was abysmally low. Back then, only 17 percent knew Burger King.
There were three more layers stacked against the newbie. The brand didn’t play the price warrior. A Whopper carried tags of Rs109 and Rs119 for vegetarian and chicken variants, respectively, and two entry-level products of Burger King—crispy veg and crispy chicken burgers—were priced at Rs45 and Rs69, respectively. Compare it with Big Mac’s blockbuster offerings: Aaloo tikki burger and chicken burger could be bought for under Rs30 and Rs50, respectively. Another impediment for Burger King was that it didn’t woo kids. It was positioned for millennials. At a time when the leader brand made it big by talking to kids and the family, Burger King’s strategy was counter-intuitive and seen as counterproductive. The last big spanner was a centralised structure. Burger King India had pan-India rights for the brand. McDonald’s or KFC or Subway, in contrast, had multiple partners, which aided a faster pace of expansion. Burger King followed the path of Jubilant FoodWorks, the master franchisee of Domino’s in India, by focusing on company-owned stores.
Despite the odds, Rajeev Varman was unfazed. “It doesn’t matter when you come in,” says the chief executive officer of Burger King India, who armed himself with just one weapon: A focussed plan. “We had planned for 10 years.” When Burger King opened its maiden outlet in November, the company hired a chief financial officer, a chief operating officer, a chief human resources officer and a battery of chefs. When one puts together a massive team, Varman underlines, one can’t grow slowly. “You don’t take four years to aim and shoot,” he says. “We shoot and then aim on the way.”
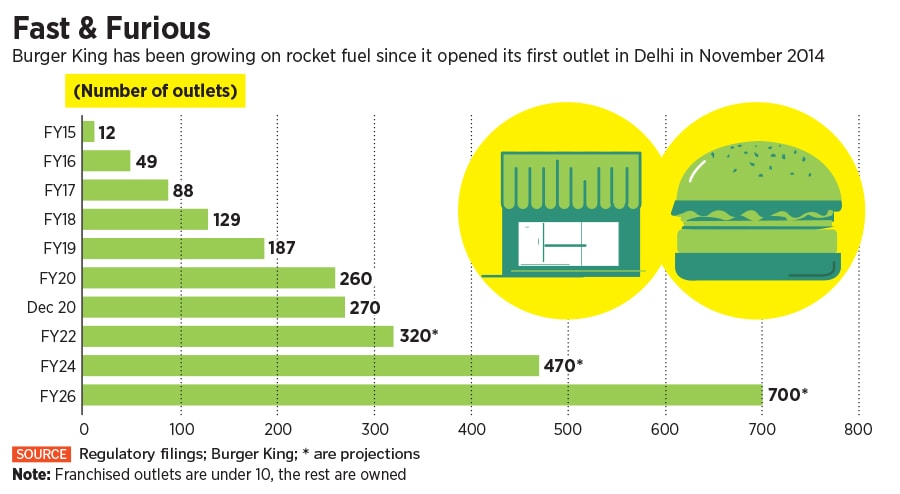
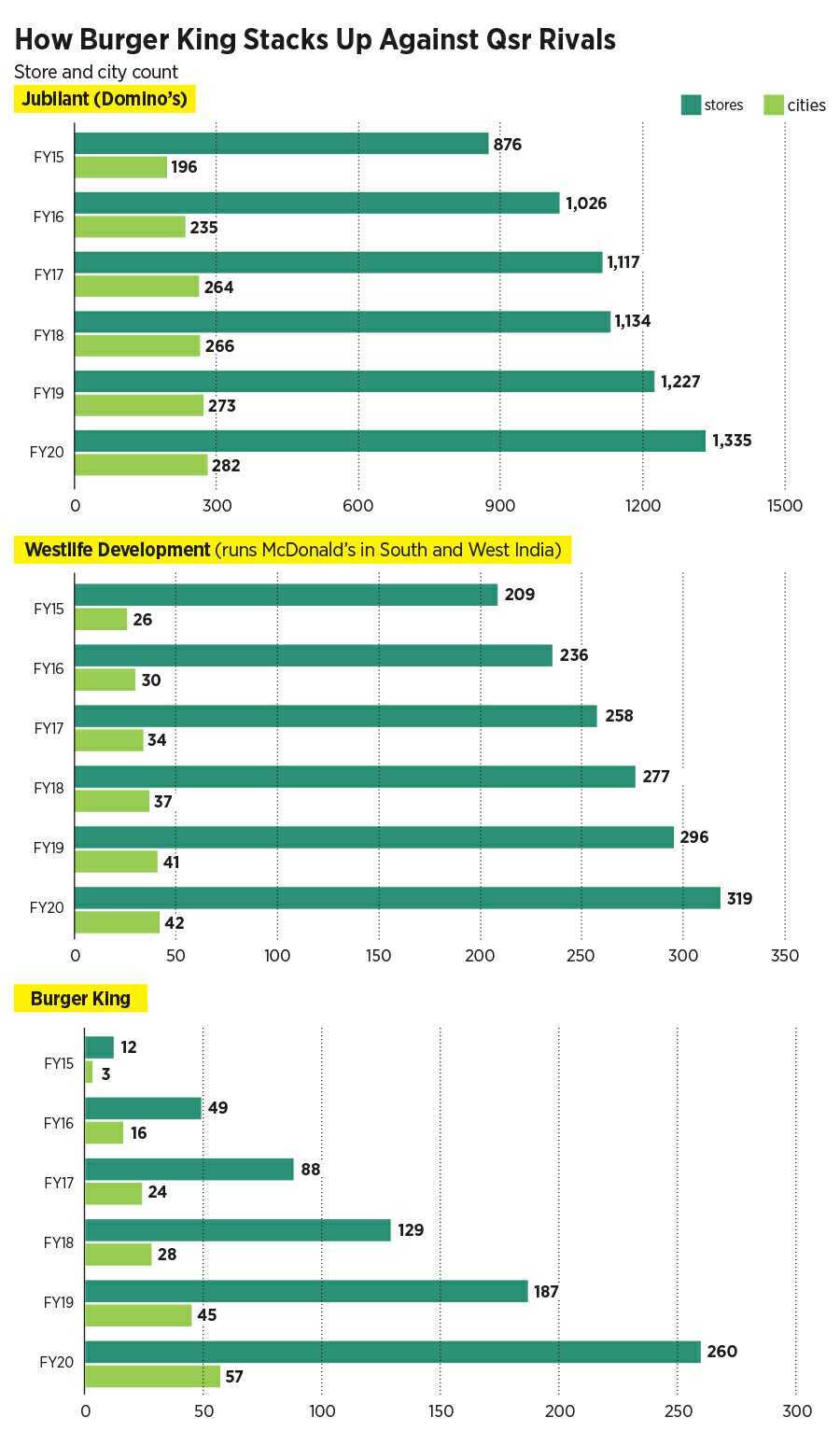
Burger King came out all guns blazing. From just 12 outlets across three cities in five months in March 2015, the Whopper maker ended FY16 with 49 stores in 16 cities. The juggernaut was just gathering steam. The store count in the next fiscal almost doubled to 88. Then it pole-vaulted to 187 in FY19 and closed FY20 at 260 with a presence across 57 cities. Compare this with McDonald’s Westlife Development, which had 209 outlets in FY15 in the West and South. Five years later, this went up to 319 stores. Add 150-odd stores in the North and East, and the combined tally was at 469. Playing catch-up at a furious pace, Burger King managed to erase more than half of the deficit in six years. In fact, it has become the fastest QSR (quick service restaurant) brand in India to clock 200 stores in a little over five years. Varman, though, is not shouting from the rooftops. “It’s just a number. Someone will break it tomorrow, and day after tomorrow, someone else will do it.”
For the time being, what Varman is more focussed on is breaking the induced lull due to Covid-19; the brand ended calendar 2020 with 270 stores, an addition of just 10 since March 2020, without entering new cities. The plan now is to go back to the furious pace by adding 50 outlets in FY22, another 70 a year later, 80 more in FY24 and reach 700 by FY26. “We have a plan in place, we have a great team in place, and sitting around and waiting is not our culture,” he says in a restless tone. Coming late doesn’t matter. “You just need to take advantage of whatever you have,” he says.
The big advantage for Burger King, reckon industry analysts, is the compelling recipe that it has managed to churn out. In its latest report on the QSR segment released last month, brokerage firm Edelweiss lists out what has worked for Burger King. “A strong brand, a favourable master franchise agreement, reasonable store economics and a customer proposition focussed on value and wide offerings have ensured success for the last major QSR entrant in India,” underlined a report titled ‘QSR: The Right Combo’. Burger King’s customer proposition focussed on value and wide offerings, the report pointed out, has a lasting flavour and is visible in its store productivity. The key aspect of Burger King’s story, though, is its highest store addition potential among all QSR players.
What makes the headroom for growth more appealing for branded QSR players, including Burger King, is a set of favourable factors for growth in a post-Covid era. Even after two decades, the Edelweiss study maintains, India’s chain QSR sector has clocked a compound annual growth of 19 percent in the FY15-20 period. One of the fastest-growing consumer discretionary categories, QSR penetration has been driven by a slew of pluses such as younger demographics, India-centric offerings, value pricing, online food delivery, and a strong marketing push. Global QSR chains have captured a much higher market share—over 50 percent of branded QSR—due to a high brand pull, fast food cuisines and expansion into Tier II and III cities. This is what helped the global chain players rebound better than the rest. While the entire food service market plunged 82 percent year-on-year in the first half of FY21, the contraction of organised QSRs (Domino’s, Burger King, and Westlife Development) was just 45 percent, and by September, recovery was at 85 percent. Burger King, for its part, was back to 85 percent of average daily sales by January this year.
Varman decodes the magic sauce, which boils down to following the three ‘Hs’ to the tee: Humility, hunger and hard work. “Humility to learn, hunger to grow, and hard work when no one is watching are the three pillars of the DNA of Burger King,” he outlines. “I never say we are the fastest to reach ‘x’ number of stores.” Arrogance, he lets on, takes away one’s ability to see, hear and listen. “We learnt from customers and competition,” he adds. Take, for instance, rolling back the ‘Rice Meal’. The move happened because the brand listened to consumers’ feedback. “In India, people want spicy, juicy and crispy,” he says, sharing one of the top learnings over the last six years. 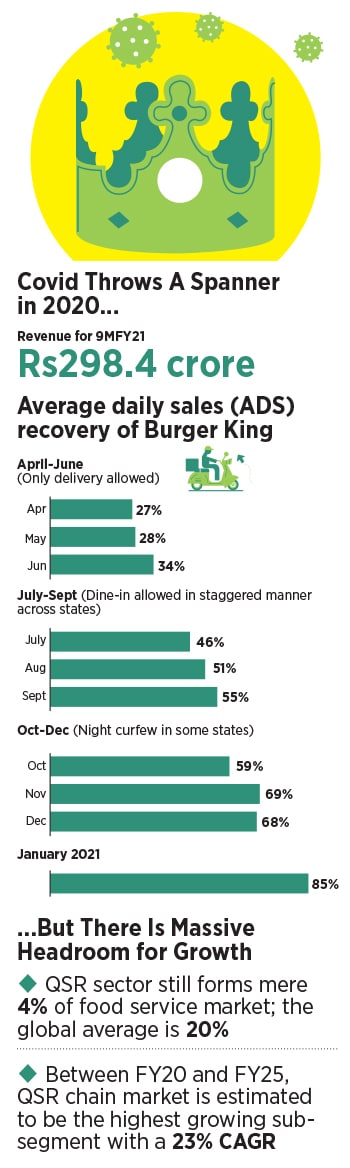 The biggest learning for Burger King, though, was to steer clear of the multiple franchisee route. In spite of a presence of over two decades, McDonald’s had paid a heavy price as the North and East Indian franchisee locked horns with the parent company in a losing war for over a decade. For a new brand coming to India, explains Varman, the first thing is to build the brand. “You don’t start with building business. You start with brand,” he says. And the best way to build, he explains, is to have complete control over growth. Burger King did two crucial things. It focussed heavily on company-owned stores. Still, after six years, the brand has just under 10 outlets managed by franchisees. “You don’t come in and start by distributing franchises all over the place,” he says.
The biggest learning for Burger King, though, was to steer clear of the multiple franchisee route. In spite of a presence of over two decades, McDonald’s had paid a heavy price as the North and East Indian franchisee locked horns with the parent company in a losing war for over a decade. For a new brand coming to India, explains Varman, the first thing is to build the brand. “You don’t start with building business. You start with brand,” he says. And the best way to build, he explains, is to have complete control over growth. Burger King did two crucial things. It focussed heavily on company-owned stores. Still, after six years, the brand has just under 10 outlets managed by franchisees. “You don’t come in and start by distributing franchises all over the place,” he says.




 What also aided Burger King, reckon marketing experts, in its aggressive expansion was a realisation that burger crown was headless in the recent past. Unlike pizza, where Domino’s has a staggering domination with over 70 perecnt share of the organised segment, the bun-patty market had been in disarray due to the war between the master franchisee of McDonald’s in North and East India and the parent company. The infighting not only left a bad taste among consumers, who were shocked by reportedly falling quality standards of food and sabotage accusations hurled by the partners, but it also left the North Indian market wide open for any rival with might.
What also aided Burger King, reckon marketing experts, in its aggressive expansion was a realisation that burger crown was headless in the recent past. Unlike pizza, where Domino’s has a staggering domination with over 70 perecnt share of the organised segment, the bun-patty market had been in disarray due to the war between the master franchisee of McDonald’s in North and East India and the parent company. The infighting not only left a bad taste among consumers, who were shocked by reportedly falling quality standards of food and sabotage accusations hurled by the partners, but it also left the North Indian market wide open for any rival with might.
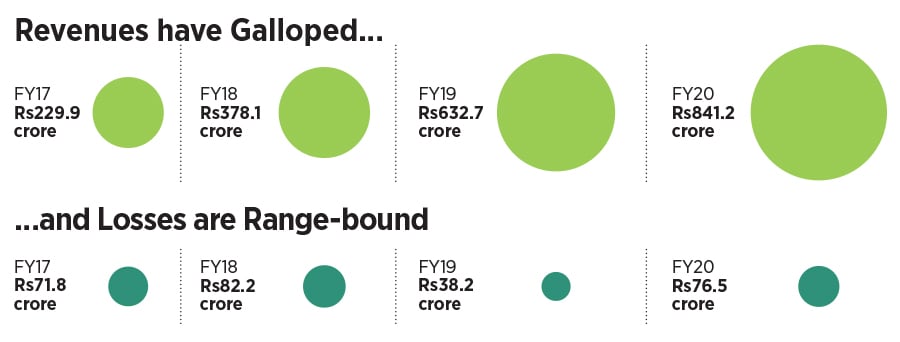
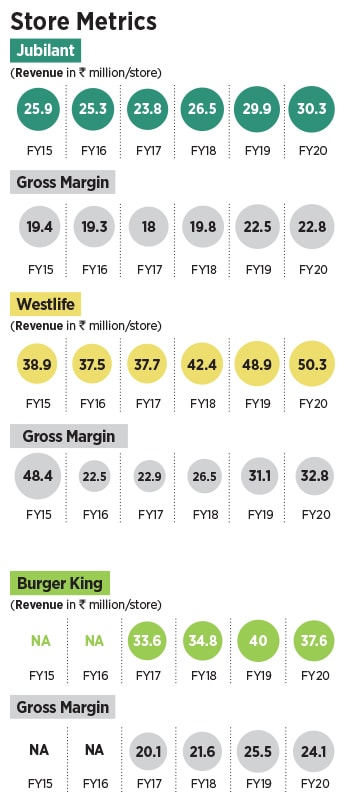
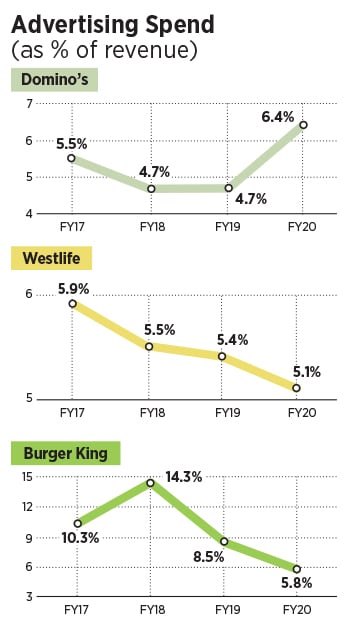 The going, though, might not be easy. QSR, point out industry analysts, is an operationally intensive business with millions of moments of truth via interactions with the customers on a daily basis. “Burger King needs to ensure that it has a good trained staff so that customer service stays exemplary,” says KS Narayanan, a food and beverage expert. He sounds a word of caution for the brand. As costs of operations inch upwards every year, he underlines, it is critical that same store sales growth is delivered on a consistent basis to ensure that unit economics remain positive. Though Burger King has seen its revenue grow at a faster clip, it’s still dealing with losses. Edelweiss too points out the flip side in its report. Domino’s, it underlined, is by far the most profitable and successful QSR in India driven by high store throughput and margins. “Limited store capex is driven by smaller store size as business is delivery-driven,” it added. Burger QSRs, it highlighted, have larger store sizes due to more kitchen space requirement, and a dine-in focus. “This drives store capex higher and returns lower,” it concluded.
The going, though, might not be easy. QSR, point out industry analysts, is an operationally intensive business with millions of moments of truth via interactions with the customers on a daily basis. “Burger King needs to ensure that it has a good trained staff so that customer service stays exemplary,” says KS Narayanan, a food and beverage expert. He sounds a word of caution for the brand. As costs of operations inch upwards every year, he underlines, it is critical that same store sales growth is delivered on a consistent basis to ensure that unit economics remain positive. Though Burger King has seen its revenue grow at a faster clip, it’s still dealing with losses. Edelweiss too points out the flip side in its report. Domino’s, it underlined, is by far the most profitable and successful QSR in India driven by high store throughput and margins. “Limited store capex is driven by smaller store size as business is delivery-driven,” it added. Burger QSRs, it highlighted, have larger store sizes due to more kitchen space requirement, and a dine-in focus. “This drives store capex higher and returns lower,” it concluded. 



